Generate and Analyse Urban 3D Model
- 1.) Install the envuo library as instructed in (https://github.com/chenkianwee/envuo)
- i.) In the previous section QGIS generates 4 shapefiles. Specify the shapefiles in the envuo\examples\convert_shp2citygml_asim.py script. Specify the result citygml file. Run the script.
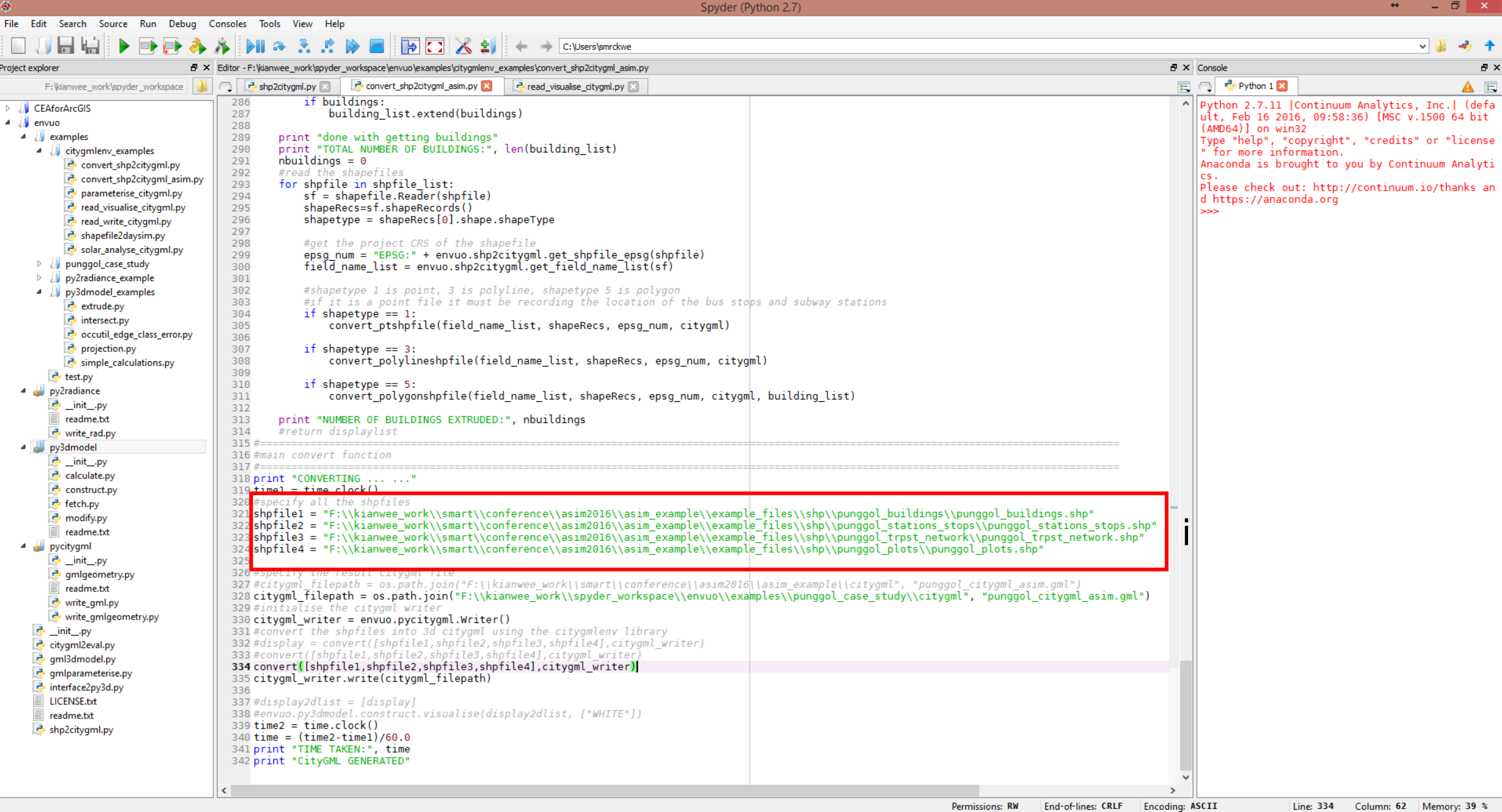
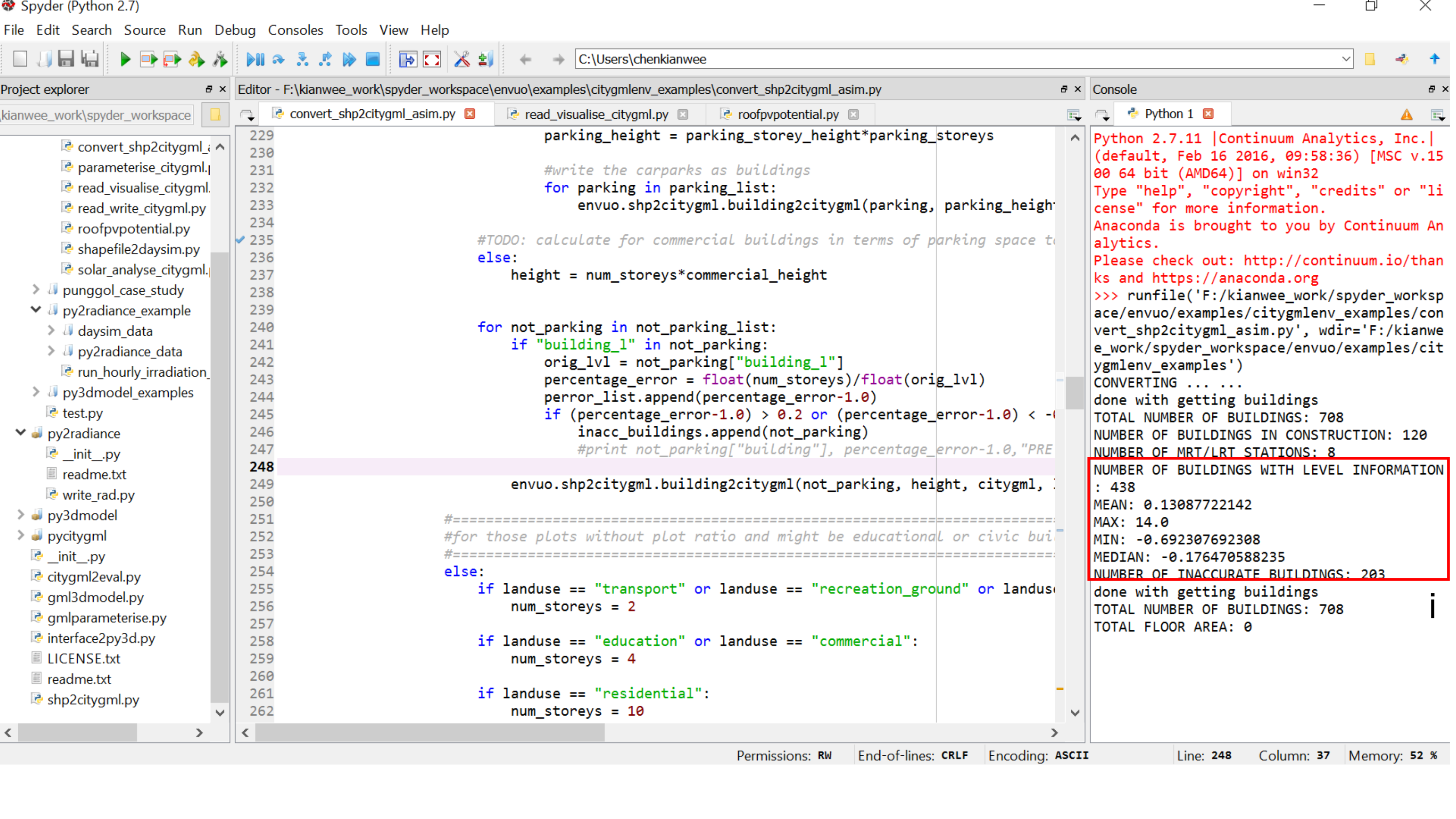
- 2.) The script checks the number of buildings with building level information. The shapefile stores the information in the attribute "building_l". The script compares the predicted height against the actual height. It then reports on the accuracy of the generated urban 3D model by consolidating the errors.
- i.) The script informs the mean, maximum, minimum, and median of their height error. It also informs the number of buildings with height information. The script counts the number of inaccurate buildings. A building is inaccurate when the predicted height differs from the original height by 20%. A Citygml file based on the actual building height is also generated if the information is available.
- 3.) Specify the citygml file in the "envuo\examples\read_visualise_citygml.py" script. Run the script.
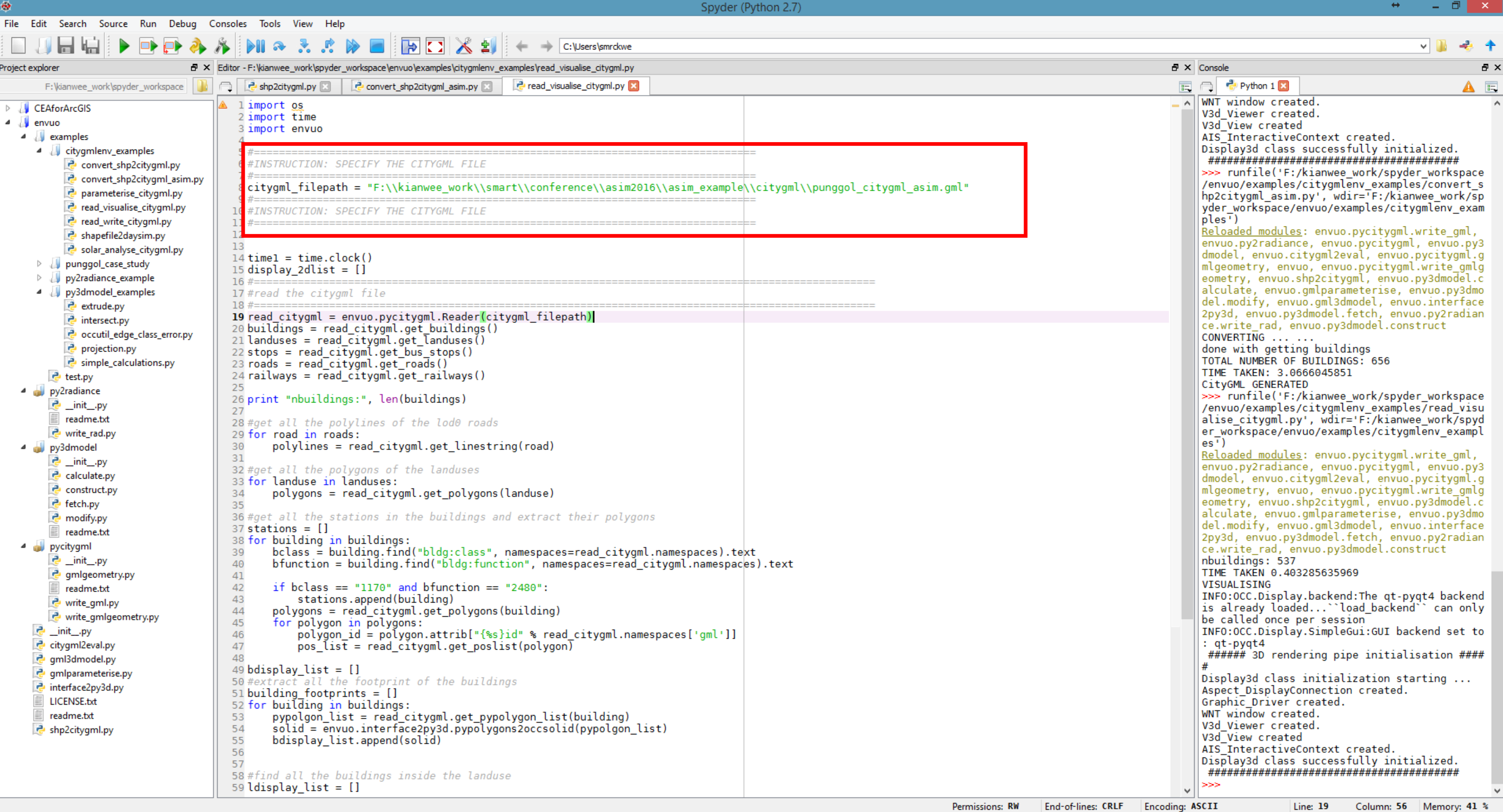
- 4.) The script generates a 3D model. Check if there are any mistakes with the 3D model. Edit and adjust until it is satisfactory. For example, the script generated a super-highrise building which is not present in Punggol. Check on the mistake and make changes to correct the mistake.
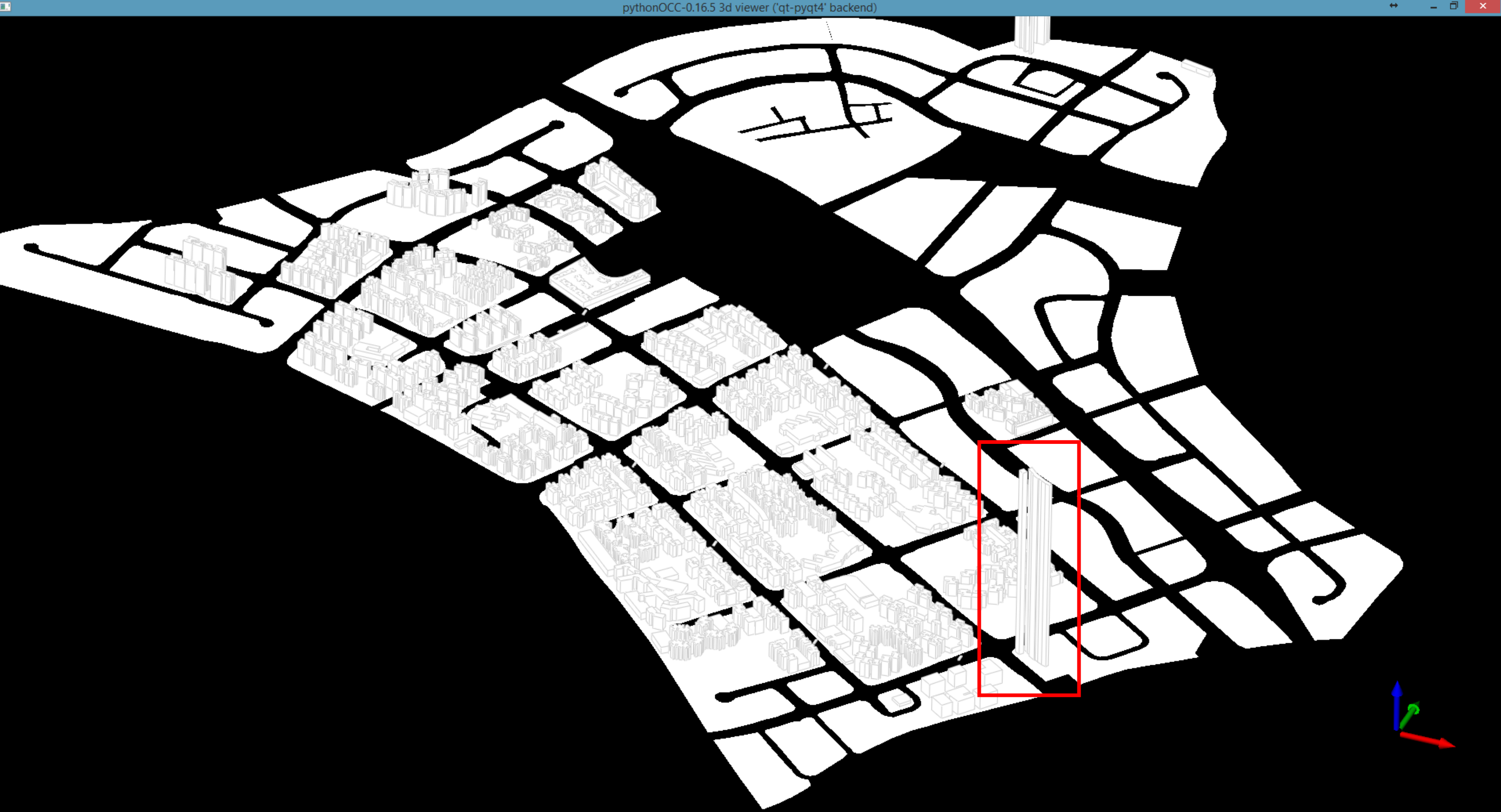
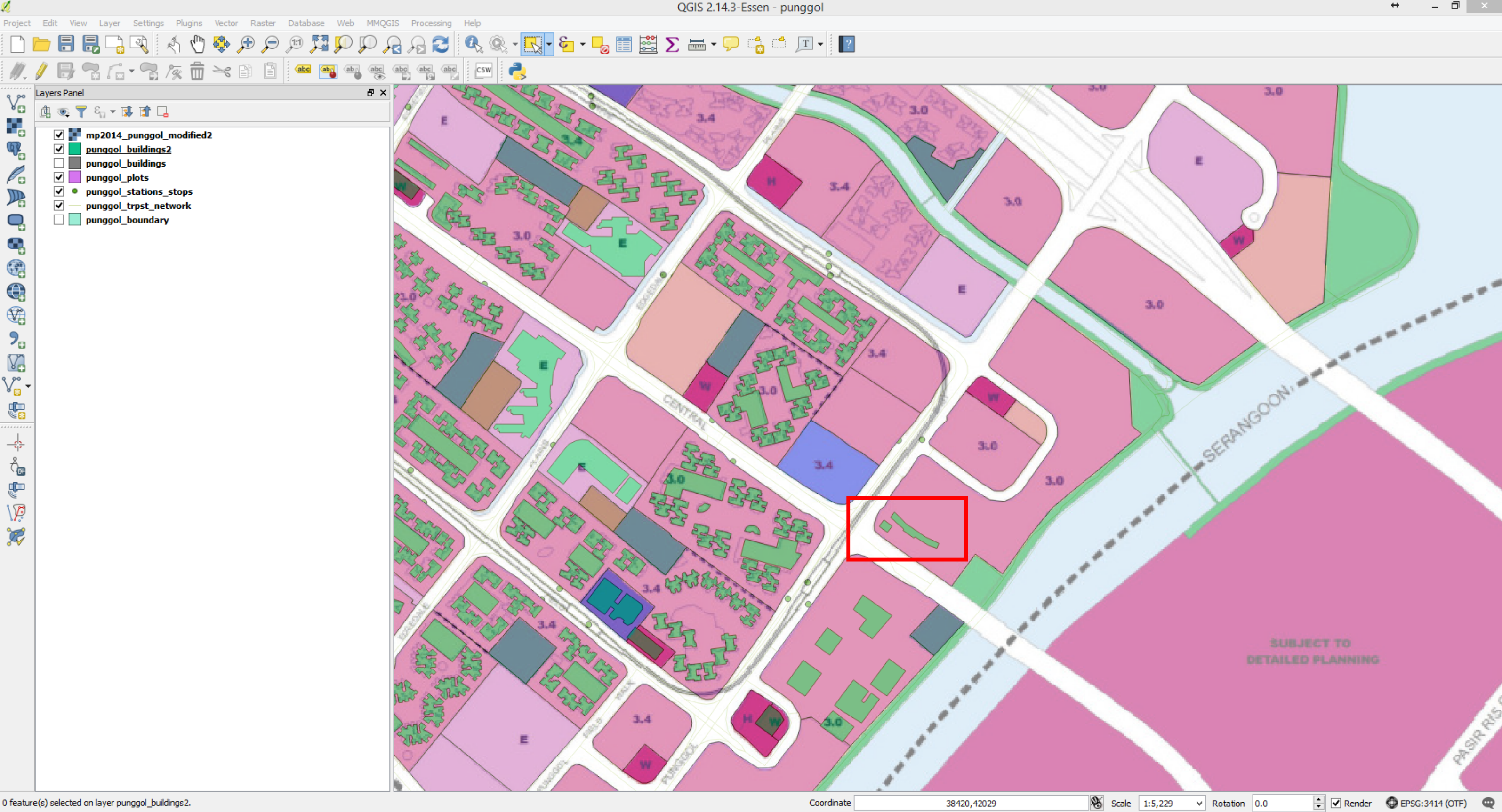
- 5.) From google map, the buildings are commercial. The plot is labelled as residential. Correct the plot to commercial. Since there are no other buildings on the plot, the extrusion will not work. Remove the plot ratio attribute and set it to NULL. Adjust and correct any other plots with error
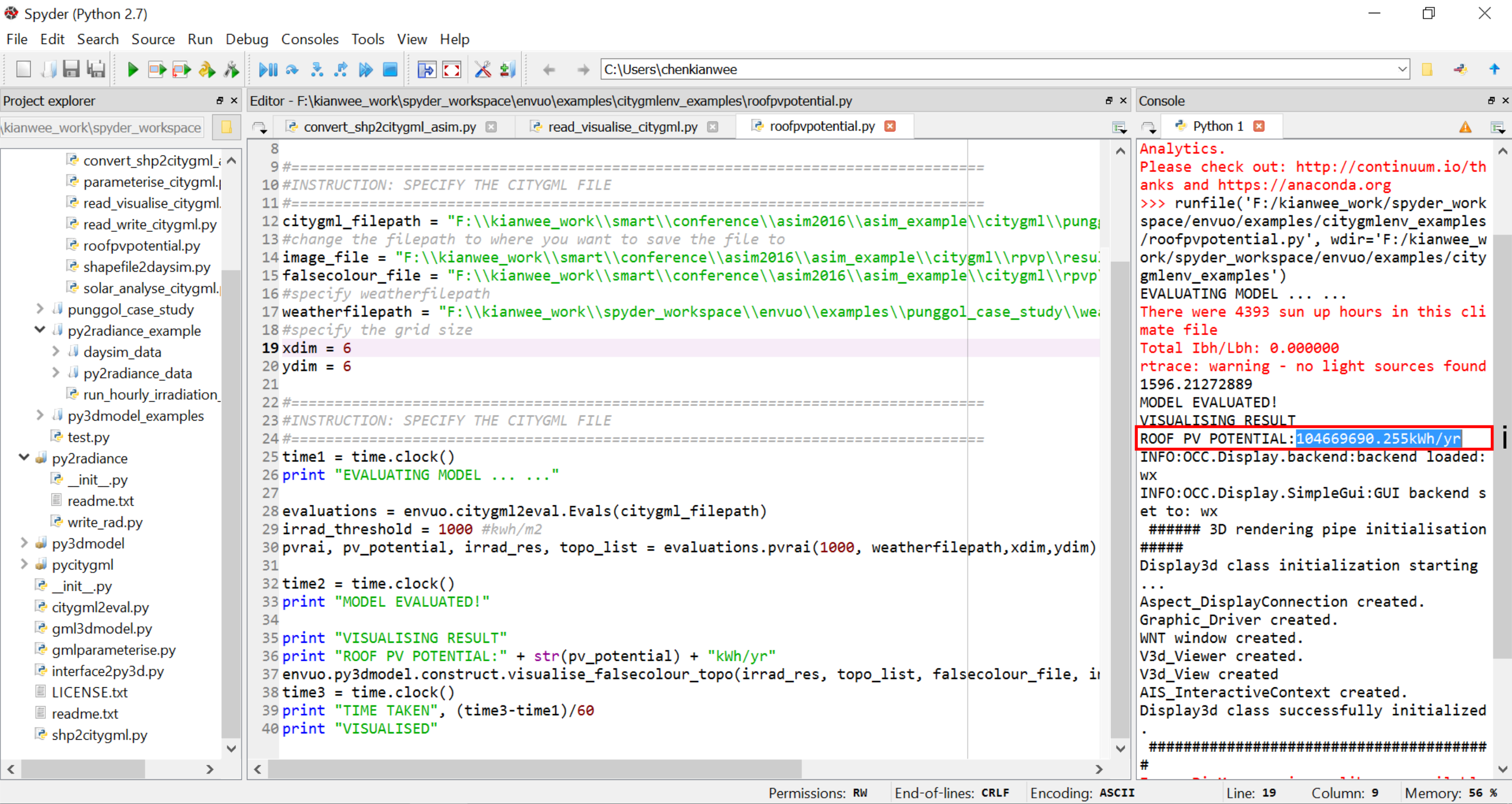
- 6.) Specify the citygml file in the "envuo\examples\roofpvpotential.py" script. Run the script.
- i.) The script simulates the roof pv potential in kWh/yr.